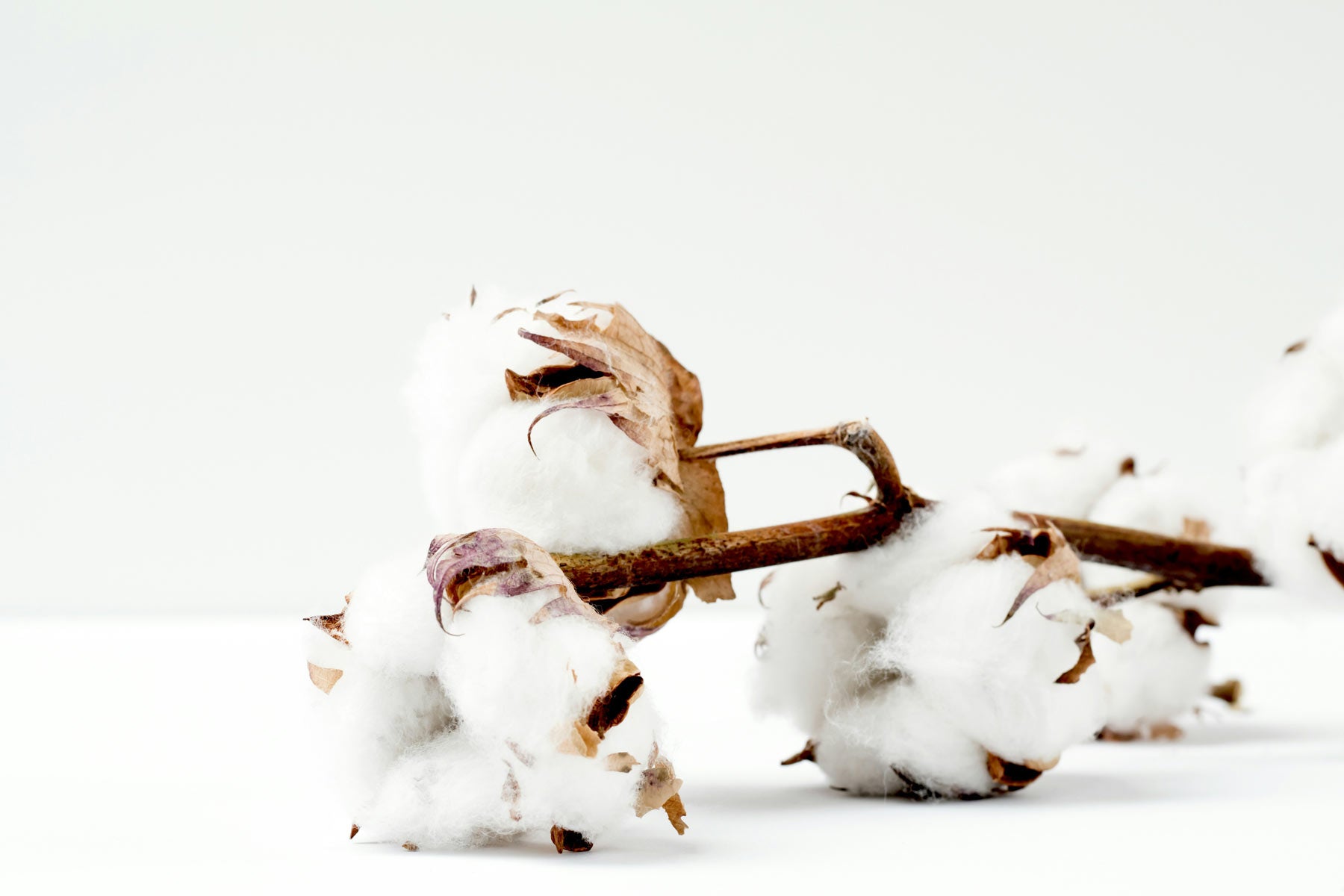

Cotton from regenerative agriculture
Since Muntagnard was founded, cotton has always been the focus. At first we didn't want to use any cotton at all for ecological reasons, then we only focused on very exclusive and specific cotton from Greece and now we are convinced that we have to actively work towards sustainable cotton. To this end, we see cotton from regenerative agriculture as a future-oriented path that is significantly more far-reaching than, for example, conventional organic cotton. Because regenerative cotton, as the name suggests, actively contributes to the regeneration of nature. But what exactly makes this form of cotton production so special and how does it differ from conventional cultivation methods?
What is regenerative agriculture?
At its core, regenerative agriculture aims not only to preserve soils, but to actively improve them. Conventional agriculture often relies on monocultures, chemical fertilizers and pesticides, which in the long term leads to soil depletion, species loss and increased CO2 emissions. In contrast, regenerative agriculture uses natural methods such as crop rotation, composting, agroforestry and the avoidance of chemical substances to promote biodiversity, improve water management and store carbon in the soil. This not only makes the soil more fertile, but can also actively contribute to mitigating climate change.
The difference between conventional and organic cotton
Conventional cotton is usually produced using chemical pesticides, herbicides and artificial fertilizers, which depletes the soil and makes it infertile in the long term. In addition, there is enormous water consumption: conventional cotton production is one of the most water-intensive forms of cultivation in the world.
Organically grown cotton is a step in the right direction, as it does not use chemical substances. It is grown according to stricter ecological standards, using only natural fertilizers and environmentally friendly methods. But even organic farming often only maintains the status quo of the soil without actively promoting its regeneration.
This is where regenerative cotton comes in. Compared to organic cotton, regenerative agriculture is about improving soil quality and revitalizing the ecosystem.
The Benefits of Cotton from Regenerative Agriculture
Cotton from regenerative agriculture therefore offers numerous advantages that benefit both the environment and people:
- Improving soil quality: Using regenerative farming methods makes the soil more fertile in the long term, which not only increases yields but also promotes biodiversity.
- Carbon storage: Regeneratively managed soils can bind large amounts of CO2 and thus actively contribute to mitigating climate change.
- Water savings: The increased water storage capacity of the soil reduces water consumption. This makes cotton cultivation in water-scarce regions more sustainable.
- Sustainable yields: Since the soils are not depleted but improved, more stable yields can be achieved in the long term without harming the environment.
- Better working conditions: Regenerative agriculture often promotes fairer working conditions for farmers because they are not dependent on expensive and often toxic chemicals and benefit from healthier soils.
The current situation on the world market
Unfortunately, despite its undeniable advantages, cotton from regenerative agriculture is still in its infancy. The majority of cotton worldwide is grown conventionally. Organic cotton only accounts for a few percent of global production, and the share of regenerative cotton is even lower - it is estimated to be less than 0.1%.
This low level of adoption is mainly due to the higher effort and conversion costs, which initially represent a hurdle for farmers. At the same time, the right incentives and awareness on the part of consumers are often still lacking to promote this form of agriculture on a large scale. But experts agree: regenerative cotton could make an important contribution to sustainable fashion production if it receives more support.
Regenerative Agriculture as the Future for Natural Fibers
The fashion industry is at a crossroads. Conventional methods are causing lasting damage to our environment, and the need for alternatives is becoming increasingly urgent. Cotton from regenerative agriculture shows a clear path to a more sustainable future that both protects nature and supports the people who cultivate it. At the same time, the conversion and production according to regenerative standards is complex, costly and not easy to implement everywhere. Meeting the current demand for cotton, for example, exclusively from regenerative agriculture seems pretty impossible. For this reason, not only the production side must be addressed, but the general demand for cheap fibers must also be reduced in order to have a substantial impact.
While regenerative cotton is still a rare commodity today, there is hope that more and more producers and consumers will recognize the benefits and choose this form of cotton. By choosing products from regenerative agriculture, we as consumers can not only consume fashion more consciously, but also contribute to the preservation and restoration of our soils.
At Muntagnard, we want to rethink fashion and promote sustainable solutions. Therefore, whenever possible, we use fibers from regenerative agriculture to actively make our contribution. We started with our polo shirts for men and women and are now gradually switching to this new type of fiber production. Our latest development made from regenerative cotton is the MANGOLA Regenerative Sweatshirt , where we combine the most sustainable cultivation methods with modern style and maximum comfort.
Click here to see the current products made from regenerative cotton
Polo Shirt - Women















Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.